# Elasticsearch Analyzer
Elasticsearch 中的分析器,是為什麼 Elasticsearch 能夠作為搜尋引擎的關鍵,在將 Document 加入 index 前,會先透過 Analyzer 將 Document 進行拆解(過濾、分詞),並建立反向索引,以便 Elasticsearch 透過反向索引進行字詞搜尋
# Analyzer 基本
在 elasticsearch 分析器的基本流程為 Character Filter > Tokenizer > Token Filter
- Character Filter : 過濾,根據所選的 character filter 會將不需要的字符給過濾掉;etc : HTML標籤,標點符號
- Tokenizer : 分詞,每個分析器必備的流程,負責重要的分詞處理
- Token Filter : 將分詞後的 Token 做個別處理;etc :大小寫轉換
# Analyzer 使用
使用一個簡單的範例來看看 Elasticsearch 是如何分詞的,先將 The Old Man and the Sea 插入索引中
POST book/_doc/1
{
"title":"The Old Man and the Sea"
}
接著使用下列API,查詢分詞結果
GET <index>/_analyze
{
"field": "欄位名",
"text": "內容"
}
GET book/_analyze
{
"field": "title",
"text": "The Old Man and the Sea"
}
elasticsearch 中預設的 analyzer 是 "analyzer" : "standard",會將所有的字詞進行拆分,結果如下:
{
{
"tokens" : [
{
"token" : "the",
"start_offset" : 0,
"end_offset" : 3,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 0
},
{
"token" : "old",
"start_offset" : 4,
"end_offset" : 7,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 1
},
{
"token" : "man",
"start_offset" : 8,
"end_offset" : 11,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 2
},
{
"token" : "and",
"start_offset" : 12,
"end_offset" : 15,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 3
},
{
"token" : "the",
"start_offset" : 16,
"end_offset" : 19,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 4
},
{
"token" : "sea",
"start_offset" : 20,
"end_offset" : 23,
"type" : "<ALPHANUM>",
"position" : 5
}
]
}
}
也可以直接指定 Analyzer 做測試
GET _analyze
{
"analyzer": "分析器種類",
"text" : "內容"
}
GET _analyze
{
"analyzer": "standard",
"text" : "The Old Man and the Sea"
}
# 內建分析器
Elasticsearch 內建幾個分析器如下:
- Standard Analyzer
- Simple Analyzer
- Whitespace Analyzer
- Stop Analyzer
- Keyword Analyzer
- Pattern Analyzer
- Language Analyzers
- Fingerprint Analyzer
另外可以自定義 Custom analyzer 文件來源 (opens new window)
稍微整理一下內建分析器的 Example output ,都是以官方範例 "The 2 QUICK Brown-Foxes jumped over the lazy dog's bone." 為基準,只是放在一起比較容易比較其中差異 :
# Standard Analyzer
預設的 Analyzer 若無特別指定就是這個,直接切分;小寫顯示
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "standard",
"text": "The 2 QUICK Brown-Foxes jumped over the lazy dog's bone."
}
輸出:
[ the, 2, quick, brown, foxes, jumped, over, the, lazy, dog's, bone ]
# Simple Analyzer
The simple analyzer breaks text into tokens at any non-letter character, such as numbers, spaces, hyphens and apostrophes, discards non-letter characters, and changes uppercase to lowercase. 將 Text 以數字、空白、符號分詞,並刪去非字母的文字;小寫顯示
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "simple",
"text": "The 2 QUICK Brown-Foxes jumped over the lazy dog's bone."
}
輸出:
[ the, quick, brown, foxes, jumped, over, the, lazy, dog, s, bone ]
# Whitespace Analyzer
The whitespace analyzer breaks text into terms whenever it encounters a whitespace character.
簡單粗暴,遇到空白就斷詞;不轉小寫
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "whitespace",
"text": "The 2 QUICK Brown-Foxes jumped over the lazy dog's bone."
}
輸出
[ The, 2, QUICK, Brown-Foxes, jumped, over, the, lazy, dog's, bone. ]
# Stop Analyzer
The stop analyzer is the same as the simple analyzer but adds support for removing stop words. It defaults to using the english stop words.
與 simple analyzer 相同,但多了過濾 Stop Analyzer 使用 _english_ 來過濾特定的 stop words(停用詞)
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "stop",
"text": "The 2 QUICK Brown-Foxes jumped over the lazy dog's bone."
}
輸出結果將 the;2 停用詞過濾掉了 有一個章節專門描述停用詞 (opens new window)
[ quick, brown, foxes, jumped, over, lazy, dog, s, bone ]
# Keyword Analyzer
The keyword analyzer is a “noop” analyzer which returns the entire input string as a single token.
一句話總結:就是【不分詞】
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "keyword",
"text": "The 2 QUICK Brown-Foxes jumped over the lazy dog's bone."
}
輸出
[ The 2 QUICK Brown-Foxes jumped over the lazy dog's bone. ]
# Pattern Analyzer
The pattern analyzer uses a regular expression to split the text into terms. The regular expression should match the token separators not the tokens themselves. The regular expression defaults to \W+ (or all non-word characters).
以正則表示式作為分詞依據,預設是 \W+,很玄幻的分析器有機會用到在特別紀錄
POST _analyze
{
"analyzer": "pattern",
"text": "The 2 QUICK Brown-Foxes jumped over the lazy dog's bone."
}
輸出
[ the, 2, quick, brown, foxes, jumped, over, the, lazy, dog, s, bone ]
# Language Analyzers
A set of analyzers aimed at analyzing specific language text
特定語言的分析器,支援的語言點這裡 (opens new window) 然後沒有中文,中文在ES中是特別的存在,開一節特別紀錄
# Index Mapping & Analyzer
可以在創建 Index 時 Mapping 自己想要的 Analyzer,但要注意的是 Mapping 後的欄位就不能更改其 Analyzer 了,除非使用 Reindex
# Index Mapping 基本使用
實驗一下,對 book 這個 index 新增一個 field title3 其類型為 text ;分析器為 simple
PUT /book/_mapping/
{
"properties":{
"title3":{
"type":"text",
"analyzer":"simple"
}
}
}
查詢 index mapping 的設定
GET /book/_mapping/
可以看到 Title3 的 analyzer 為 simple,第一個 Title 為預設新增的可以看到 properties 中有一個 fields 這個便是 Multi-field,下一小段說明 Multi-field
{
"book" : {
"mappings" : {
"properties" : {
"title" : {
"type" : "text",
"fields" : {
"keyword" : {
"type" : "keyword",
"ignore_above" : 256
}
}
},
"title2" : {
"type" : "text",
"analyzer" : "standard"
},
"title3" : {
"type" : "text",
"analyzer" : "simple"
}
}
}
}
}
# Multi-fields
我們可以透過分配不同的 Multi-fields 在同一個字段中使用不同的 analyzer 來提升搜尋的準確度。
- 先創建一個
index讓主要的analyzer為simple,fields中的為english
PUT /book-multi-fields
{
"mappings":{
"properties":{
"title":{
"type":"text",
"analyzer":"simple",
"fields":{
"english":{
"type":"text",
"analyzer":"english"
}
}
}
}
}
}
往 index book-multi-fields 中放入一筆資料 "title":"The Old Man and the Sea"
POST /book-multi-fields/_doc/1
{
"title":"The Old Man and the Sea"
}
接著搜尋以下三種情況:
GET /book-multi-fields/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title": "the"
}
}
}
GET /book-multi-fields/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title.english": "the"
}
}
}
GET /book-multi-fields/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"title.english": "sea"
}
}
}
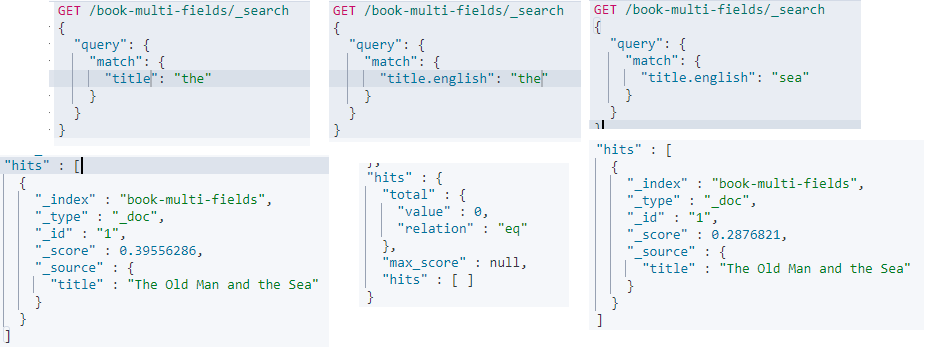
結果為第一個命中,第二個未命中,第三個命中,這是因為條件為 title 時分析器為 simple 會保留 the,條件為 title.english 時,分析器 english 會將 the 作為 stop words 過濾掉。
# 客製化 Analyzer
待補